Improving Performance of Low-Slope Roofs
Using Insulating Cover Boards












Roof systems have come under increased focus due to the energy efficiency requirements that have been enforced with the new building codes, requiring additional thermal resistance (in the form of increased R-value) and therefore increased thickness of roofs. In addition, there are other requirements that must be taken into account when designing a roof system, including fire, acoustic and expected traffic on the roof to make it more durable and resilient.
Hybrid roof systems, those that use two or more different types of insulation are becoming more popular, as designers seek to use the benefits of products to maximize performance of each type of product.
Cover boards have been used on roofs to provide a substrate for membrane attachment on top of the thermal insulation (typically polyisocyanurate or polyiso) and a surface for expected loads on the roof. When designed efficiently, coverboards have the potential to provide a number of benefits to improve the performance of the roof system.
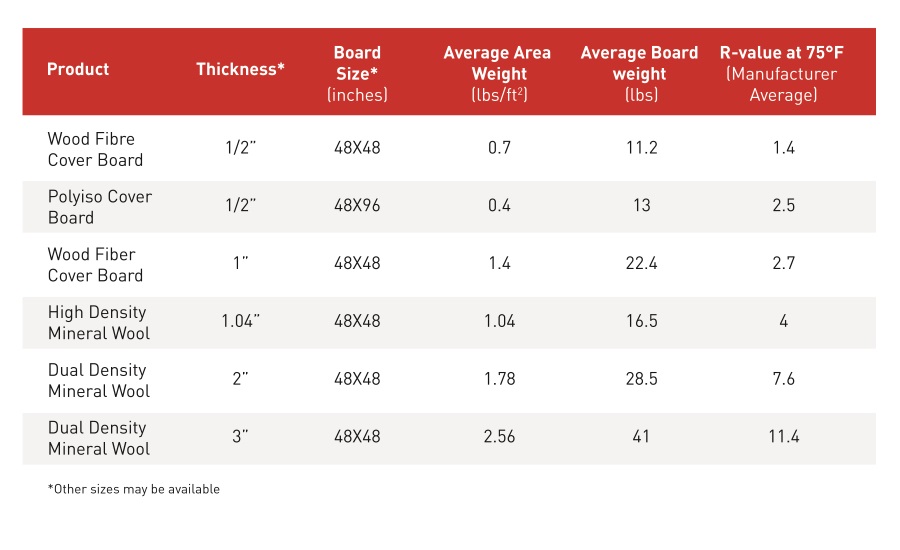
Figure 1 summarizes some of the conventional coverboard materials used.
Thermal Resistance
All building materials provide some level of thermal resistance and the measured performance of these materials are generally represented by the published R-values of the materials. Effective R-values take into account the interaction of the different materials in their environment and would need to be calculated (with performance tables or building modeling). Coverboard materials have been typically relied on for minimal R-values in the system. However, with insulating cover boards such as mineral wool, the thermal resistance of the product can reduce the demand for the typical thermal insulation to provide all of the thermal resistance and reduce the number of layers in the roof system, thereby reducing labor on the job.
Mineral wool has an R3.8-per-inch, compared to an average of R2.7-per-inch for wood fiber, allowing it to reduce the thickness of the required polyiso. In addition to the improved measured thermal resistance, mineral wool roof boards complement the polyiso by providing increased thermal performance at cold temperatures. Figure 2 shows the R-value of the two products across the four mean temperatures that are conventionally completed as part of the ASTM C518 thermal resistance test.
Mineral wool products, when used over a layer of polyisocyanurate in a hybrid roof system, assists the performance of polyiso by moderating the interface temperature the polyiso would be exposed to. This keeps the polyisocyanurate thermal insulation layer at a higher temperature range.
Figure 3, completed through WUFI 5.3 Pro modelling of 1m2 of a building, predicts the reduction of energy use (for cooling and heating) of three systems. One is a conventional R30 roof system, located in Toronto, ON, with polyisocyanurate and a wood fibre cover board, while the other two systems incorporate mineral wool insulation. All systems are utilizing a dark membrane; the membrane color will have an impact on the performance as well. As shown, the mineral wool systems increase the performance of the roof, improving thermal resistance without significantly increasing the height of the system (1/2-inch and 1-inch respectively).
Impact Resistance
During construction, cover boards have to perform their functions after being subjected to some traffic, and mineral wool cover boards perform exceptionally well with impacts. While the compressive strength of the product may be lower than other cover board materials, the dual density mineral wool boards rely on the point load resistance to maintain the integrity of the adhesion between the board and the membrane in the roof system.
The load is distributed across the entire board rather than focused on a single point which is seen in monolithic roof cover boards. This allows for improved performance and reduces the chance for damage done to the fibers. In addition, when the load is removed from the board, the board will return to its original state. National Roofing Contractor Association (NRCA) guidelines should always be followed for heavy traffic areas during construction and use of the building to prevent unnecessary damage to any part of the roof system.
The dual density attributes of the mineral wool roof board also allows for improved performance during a hail event, rating Class 1—SH (Severe Hail) for the FM 4470 Test Standard for Susceptibility to Hail Damage.
Dimensional Stability
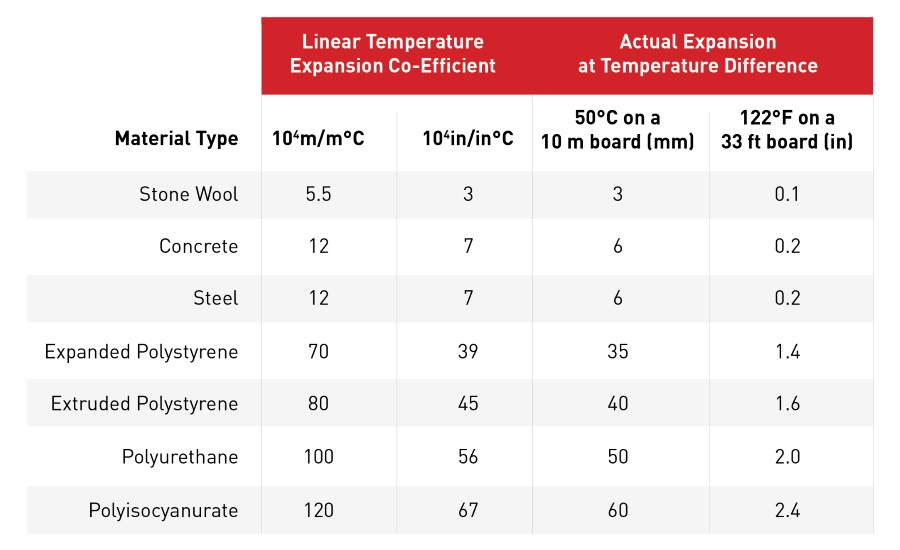
Providing a reliable substrate for the membrane is a key attribute of a cover board, as the adhesion prevents the roof from premature failure. Unnecessary stress on roof membrane can occur when the substrate moves. Due to the large variance in temperatures seen on the roof, dimensionally stable materials, such as mineral wool, perform much better than dimensionally unstable materials. Materials which are dimensional stable can limit the stress on the membrane, prolonging the lifetime of the roof system.
Dimensional stability has potential to improve the energy efficiency of the roof, as gaps in the insulation can decrease the effective performance of the system. Mineral wool roof products maintain their dimensions over thermal cycles that products are exposed to on the roof, limiting gaps and drops in the effective thermal performance. Using mineral wool products as a coverboard in a hybrid system can also improve the performance of the underlying layers by moderating the temperatures they are exposed to, decreasing the gaps in the thermal layer.
Acoustic Performance
For key areas or buildings, the acoustic performance of the roof system is an essential factor to the satisfaction of the owners and occupants. Areas with local aircraft noise, hospitals or schools can require high STC-rated roof systems in order to allow for the use of the space. In these cases, combinations of rigid and dense materials are necessary to meet the performance requirements. These systems may require the combination of high-performance acoustic solutions such as gypsum cover boards as well as mineral wool in the system to meet or surpass the acoustic and thermal requirements. Most roof board manufacturers are able to provide assistance in designing roof systems that meet or exceed these requirements.
Fire Resistance
Mineral wool roof boards can add improved fire protection in the roof system that can help limit the spread of fire or smoke on the roof. This can be particularly useful on re-roofs or critical facilities, as the building is being used during construction. Mineral wool roof boards have been tested and are the only roof products classified as FM 4470 Non-Combustible Core, for their high fire resistance.
Conclusion
An insulating coverboard can provide more than just a substrate for the membrane, and it is also an easy way to improve the performance of the roof system without moving away from designs that work. Adding mineral wool coverboard can help improve thermal performance, while providing impact resistance and dimensional stability, potentially improving the durability of the roof system. It can also provide important acoustic and safety benefits, with the added advantage of reducing time on the jobsite, waste and landfill costs. Installed as an insulating coverboard, mineral wool boards over polyiso provide many very desirable results that work together to improve building performance.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!